
Nutraceuticals represent a transformative approach to chronic disease management in 2025, bridging the gap between nutrition and pharmaceutical interventions. These bioactive compounds, derived from food sources, offer therapeutic benefits beyond basic nutrition and are increasingly recognized for their role in preventing and managing conditions like diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic syndrome. As the global burden of chronic non-communicable diseases continues to rise, nutraceuticals provide a promising alternative or complement to conventional pharmacological treatments, often with fewer side effects and better long-term sustainability.
The term “nutraceutical” combines “nutrition” and “pharmaceutical,” reflecting products that deliver medical or health benefits while serving dietary purposes. In 2025, these compounds are gaining unprecedented attention due to mounting evidence of their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, neuroprotective, and cardioprotective properties.
Key Biological Pathways
Nutraceuticals exert their therapeutic effects through multiple interconnected mechanisms that target the underlying pathophysiology of chronic diseases:
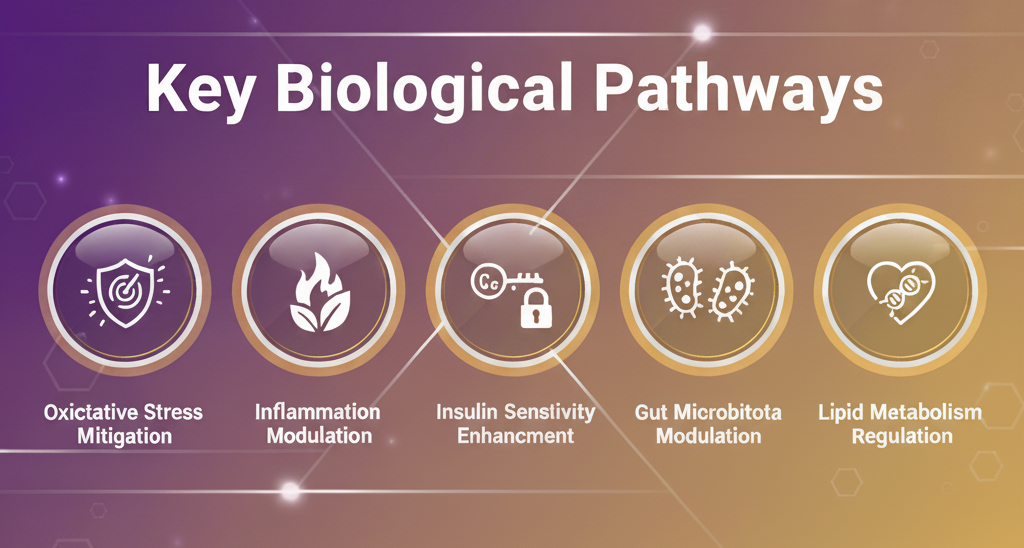
1. Oxidative Stress Mitigation
Chronic diseases like diabetes and obesity are characterized by excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduced antioxidant defenses. Nutraceuticals containing polyphenols, flavonoids, and vitamins neutralize free radicals, thereby protecting cellular structures from oxidative damage.
2. Inflammation Modulation
Low-grade chronic inflammation is a hallmark of metabolic disorders. Bioactive compounds such as curcumin, omega-3 fatty acids, and green tea catechins suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β) and activate anti-inflammatory pathways.
3. Insulin Sensitivity Enhancement
Many nutraceuticals improve glucose metabolism by enhancing insulin receptor expression, increasing glucose uptake in cells, and reducing insulin resistance. Compounds like berberine activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a master regulator of cellular energy metabolism.
4. Gut Microbiota Modulation
The intestinal microbiome plays a crucial role in metabolic health. Nutraceuticals such as probiotics and prebiotics reshape gut bacterial composition, increase beneficial bacteria like Akkermansia muciniphila and Lactobacillus species, and enhance short-chain fatty acid production.
5. Lipid Metabolism Regulation
Certain nutraceuticals inhibit fat synthesis, enhance fat oxidation, and improve lipid profiles by reducing triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, and total cholesterol while increasing HDL cholesterol.
Major Nutraceuticals for Diabetes Management
Key Nutraceuticals for Diabetes Control
| Nutraceutical | Active Compounds | Mechanisms of Action | Clinical Benefits | Recommended Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Berberine | Isoquinoline alkaloid | Activates AMPK; enhances insulin receptor expression; reduces hepatic glucose production | Reduces fasting blood glucose by 20%; lowers HbA1c by 12%; comparable to metformin | 500-1500 mg daily |
| Cinnamon Extract | Cinnamaldehyde, polyphenols | Improves insulin sensitivity; mimics insulin action | Lowers fasting glucose; reduces postprandial glucose spikes | 1-6 grams daily |
| Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA) | Antioxidant | Reduces oxidative stress; improves mitochondrial function | Treats diabetic neuropathy; enhances insulin sensitivity | 300-600 mg daily |
| Gymnema Sylvestre | Gymnemic acids | Stimulates insulin secretion; inhibits glucose absorption | Reduces blood glucose; regenerates pancreatic β-cells | 400-600 mg daily |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | EPA, DHA | Anti-inflammatory; improves lipid metabolism | Reduces triglycerides; may improve insulin sensitivity | 1-4 grams daily |
| Vitamin D | Cholecalciferol | Modulates insulin synthesis; reduces inflammation | 15% reduction in diabetes risk in prediabetes; increases reversion to normoglycemia | 2000-4000 IU daily |
| Curcumin | Polyphenol from turmeric | NF-κB inhibition; PPAR-γ activation | Reduces fasting glucose; decreases HbA1c; improves insulin resistance | 500-2000 mg daily |
How Berberine Controls Blood Sugar
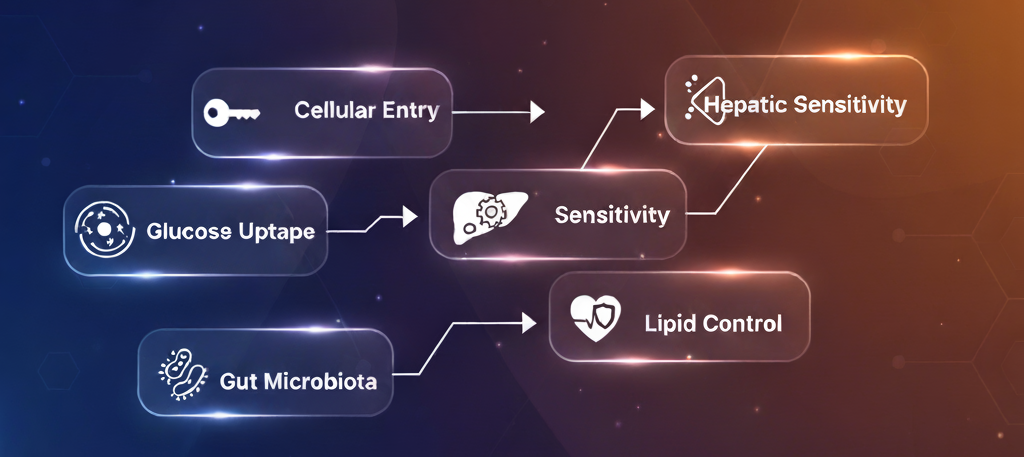
Cellular Entry: Berberine enters cells and activates AMPK, the metabolic master switch
Glucose Uptake: Increases GLUT4 transporter expression, enhancing cellular glucose uptake
Hepatic Regulation: Reduces glucose production in the liver through decreased gluconeogenesis
Insulin Sensitivity: Improves insulin receptor expression and downstream signaling
Gut Microbiota: Increases beneficial bacteria that produce metabolites improving glucose homeostasis
Lipid Control: Simultaneously reduces triglycerides and LDL cholesterol
Clinical studies demonstrate that berberine's glucose-lowering effects are comparable to metformin, with fasting blood glucose reductions of 3.7 mmol/L and HbA1c decreases of 2% over 3 months. The compound exhibits a robust safety profile with only mild gastrointestinal side effects in approximately 34% of users.
Nutraceuticals for Obesity and Weight Management
Evidence-Based Nutraceuticals for Obesity
| Nutraceutical | Primary Mechanism | Weight Loss Effects | Additional Benefits | Safety Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Tea Extract (EGCG) | Thermogenesis; fat oxidation enhancement | 0.9-2.5 kg weight loss over 12 weeks; reduces waist circumference | Lowers cholesterol; regulates ghrelin and adiponectin | Well-tolerated; no adverse effects at 856 mg daily |
| Probiotics (Lactobacillus gasseri) | Gut microbiota modulation; fat absorption inhibition | Reduces body weight, BMI, waist circumference, visceral fat | Decreases inflammation; improves metabolic markers | Safe for long-term use |
| Glucomannan | Viscosity-induced satiety; delayed gastric emptying | 0.79 kg weighted mean difference vs. placebo | Reduces cholesterol; improves glycemic control | May cause GI discomfort |
| Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) | Reduces fat synthesis; enhances lipolysis | Modest fat loss; reduced fat accumulation | Improves body composition | Generally safe at recommended doses |
| Garcinia Cambogia (HCA) | Inhibits citrate lyase; suppresses appetite | Mixed results; requires more research | May reduce fat synthesis | Short-term use appears safe |
| Dietary Fiber Supplements | Satiety enhancement; reduced calorie absorption | 4.4 lbs over 20 months with 8g increase per 1000 kcal | Improves cholesterol; regulates blood glucose | Safe; high doses may cause bloating |
The Role of Green Tea Extract in Weight Management
Green tea extract, particularly its main bioactive catechin epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), has emerged as one of the most researched nutraceuticals for obesity management in 2025. A randomized controlled trial involving 102 women with central obesity demonstrated significant benefits:

Weight Loss: 1.1 kg reduction over 12 weeks
Waist Circumference: Significant decrease from baseline
BMI Reduction: Statistically significant improvement
Hormonal Changes: Decreased ghrelin (appetite hormone) and increased adiponectin (metabolic regulator)
Lipid Profile: 5.33% reduction in total cholesterol and decreased LDL levels
The mechanisms involve increased thermogenesis (heat production from calorie burning), enhanced fat oxidation, and inhibition of enzymes that break down norepinephrine, thereby prolonging its fat-burning effects.
Probiotics and Gut Health in Obesity
The gut microbiota dysbiosis observed in obesity characterized by increased Firmicutes and decreased Bifidobacterium contributes to metabolic dysfunction. Probiotic supplementation offers multiple benefits:
- Reduce dietary fat absorption by 20-30%
- Release appetite-suppressing hormones (GLP-1, PYY)
- Increase fat-regulating proteins (ANGPTL4)
- Reduce systemic inflammation through improved gut barrier function
- Produce short-chain fatty acids that regulate energy metabolism
A meta-analysis of 38,802 adults found that probiotic consumption was associated with 13.1% lower obesity prevalence and significantly reduced BMI.
Nutraceuticals for Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome characterized by abdominal obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension affects millions globally. Nutraceutical combinations show particular promise for this multifaceted condition.
Combination Nutraceutical Formulations for Metabolic Syndrome
| Formulation Components | Clinical Outcomes | Study Duration | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red yeast rice + Berberine + Policosanol + Astaxanthin + CoQ10 | 11-21% reduction in total cholesterol; 15-31% reduction in LDL-C | 8-12 weeks | Comparable to low-dose statins; well-tolerated |
| Myo-inositol + Glycine + Coprinus comatus + ALA + Chromium + Vitamin B6 | Significant reduction in insulin, HOMA-IR, BMI, waist circumference, total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides | 3 months | No measurable side effects |
| Chitosan + Beta-sitosterol + Ferulic acid | Reduced liver fat, improved lipid profile, decreased insulin resistance | 12 weeks | Enhanced when combined with atorvastatin |
| Bifidobacterium longum BB536 + Red yeast rice | Improved atherogenic lipid profile in low cardiovascular risk individuals | 2 weeks | High tolerability; reduced TC and LDL-C |
Advanced Delivery Systems: Enhancing Bioavailability
A critical challenge in nutraceutical efficacy is bioavailability the proportion of the compound that enters circulation and reaches target tissues. In 2025, advanced delivery technologies are revolutionizing nutraceutical effectiveness.
Nanotechnology-Based Delivery Systems
Nanoformulation Technologies for Nutraceuticals
| Technology | Description | Advantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liposomes | Spherical vesicles with lipid bilayers | Protect hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds; enhance membrane permeability | Curcumin, omega-3, vitamins |
| Solid Lipid Nanoparticles | Solid lipid matrix at room temperature | Improved stability; controlled release; enhanced bioavailability | Fat-soluble vitamins, polyphenols |
| Nanoemulsions | Oil-in-water or water-in-oil dispersions (20-200 nm) | Increased surface area; improved absorption | Carotenoids, essential oils |
| Polymeric Nanoparticles | PLGA, chitosan-based carriers | Sustained release; targeted delivery; protection from degradation | Resveratrol, quercetin |
| Nanocurcumin | Curcumin in nanoparticle form | 16× increased bioavailability; enhanced brain penetration | Metabolic syndrome, neurodegenerative diseases |
These technologies address critical limitations such as poor water solubility, rapid metabolism, and limited absorption, significantly enhancing therapeutic outcomes.
Safety, Regulation, and Quality Standards
Regulatory Framework
The nutraceutical industry operates under evolving regulatory frameworks that vary by country
Key Regulatory Requirements (2025):
Safety Assessment: Evaluation of all active components and their interactions
Quality Standards: Standardization to marker compounds with specified daily usage levels
Labeling Requirements: Clear information on purpose, target population, dosage, duration, and contraindications
Scientific Validation: Claims must be supported by generally accepted scientific data
Manufacturing Standards: Compliance with Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP)
Adverse Event Reporting: Mandatory reporting of safety concerns
Important Restrictions:
- No hormones, steroids, or psychotropic ingredients permitted
- Cannot claim to prevent, treat, or cure specific diseases
- Must demonstrate documented history of safe use (15 years domestically or 30 years internationally)
Future Trends in Nutraceuticals: 2025 and Beyond
Personalized Nutrition and Precision Medicine
The integration of nutrigenomics, metabolomics, and microbiome profiling enables customized nutraceutical regimens based on individual genetic makeup, metabolic status, and lifestyle factors. DNA-based supplements and AI-generated recommendations are becoming mainstream.
Key Developments:
- Genetic testing to identify optimal nutraceutical responses
- Microbiome analysis for targeted probiotic selection
- Wearable technology integration for real-time monitoring
- AI-driven supplement recommendations based on biomarker data
Enhanced Clinical Validation
In 2025, rigorous clinical trials are establishing the evidence base for nutraceutical interventions:
- Large-scale, well-designed randomized controlled trials
- Dose-response studies to establish optimal intake levels
- Long-term safety monitoring and efficacy assessment
- Biomarker-based outcome measurements
Sustainable and Plant-Based Innovation
Consumer demand for clean-label, transparent, and sustainably sourced products drives innovation in plant-based nutraceuticals:
- Clinical validation of traditional botanicals (turmeric, ashwagandha, amla)
- Emphasis on ethical sourcing and eco-friendly packaging
- Plant-based alternatives to synthetic supplements
Advanced Delivery Formats
Moving beyond traditional pills and capsules:
- Gummies, powders, and liquid shots for improved compliance
- Nanotech delivery systems for enhanced absorption
- Time-release formulations for sustained effects
- Combination products targeting multiple pathways
Mental Health and Cognitive Support
Stress management, sleep quality, and cognitive function supplements represent rapidly growing segments:
- Adaptogens for stress resilience
- Nootropics for cognitive enhancement
- Natural sleep aids
- Mood-supporting botanicals
Implementing Nutraceuticals: A Practical Guide
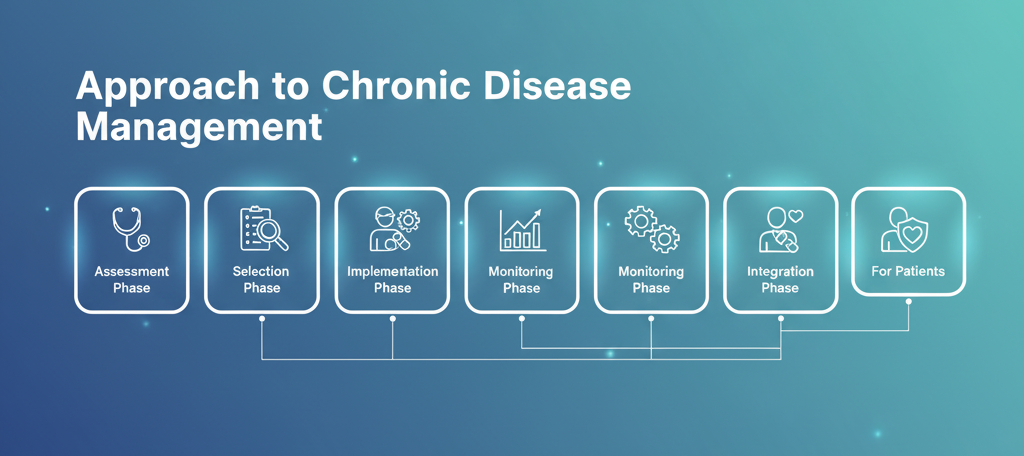
Assessment Phase
- Evaluate patient's medical history, current medications, and nutritional status
- Identify specific metabolic markers (fasting glucose, HbA1c, lipid profile, inflammatory markers)
- Screen for potential drug-nutraceutical interactions
Selection Phase
- Choose evidence-based nutraceuticals with clinical validation
- Consider bioavailability-enhanced formulations
- Select appropriate dosages based on published research
Implementation Phase
- Start with single compounds before combination products
- Monitor tolerance and initial response
- Provide clear instructions on timing, food interactions, and duration
Monitoring Phase
- Regular assessment of metabolic markers (every 3 months initially)
- Track adverse events and patient compliance
- Adjust dosages or formulations as needed
Integration Phase
- Combine nutraceutical therapy with lifestyle modifications
- Coordinate with conventional medical treatments
- Plan for long-term maintenance strategies
For Patients:
- Consult healthcare providers before starting nutraceutical regimens
- Choose products from reputable manufacturers with third-party testing
- Follow recommended dosages and timing
- Maintain consistent use for adequate therapeutic duration (typically 8-12 weeks)
- Report any adverse effects immediately
- Combine supplementation with healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management
Challenges and Considerations
Despite promising benefits, several challenges remain in nutraceutical applications:
Major Limitations:
- Bioavailability Issues: Many compounds have poor absorption and rapid metabolism
- Standardization Problems: Variability in product quality and active ingredient concentration
- Herb-Drug Interactions: Potential interference with pharmaceutical medications
- Limited Long-Term Data: Insufficient evidence on prolonged use effects
- Regulatory Inconsistencies: Varying standards across countries
- Cost Considerations: Premium formulations may be expensive
Addressing These Challenges:
- Adoption of advanced delivery technologies to enhance bioavailability
- Implementation of stringent quality control and third-party testing
- Comprehensive drug interaction databases for healthcare providers
- Investment in long-term clinical trials and post-market surveillance
- Global regulatory harmonization efforts
Conclusion: The Future of Integrative Healthcare
Nutraceuticals represent a paradigm shift in chronic disease management, offering evidence-based, safe, and sustainable alternatives or complements to conventional pharmaceuticals. In 2025, the convergence of advanced research, improved delivery technologies, personalized nutrition strategies, and rigorous clinical validation positions nutraceuticals as essential components of modern healthcare. For diabetes management, compounds like berberine, alpha-lipoic acid, and vitamin D demonstrate efficacy comparable to conventional medications while offering additional metabolic benefits.
In obesity management, green tea extract, probiotics, and dietary fibers provide multifaceted approaches to weight control by targeting appetite regulation, fat metabolism, and gut microbiota. The future landscape of nutraceuticals will be shaped by personalized precision medicine, AI-assisted discovery, nanotechnology-enhanced delivery, and global regulatory harmonization. As consumers increasingly seek natural, preventive, and holistic health solutions, nutraceuticals bridge the critical gap between nutrition and medicine, empowering individuals to take proactive roles in managing their health.
Sources
Das, L., Bhaumik, E., Raychaudhuri, U. and Chakraborty, R., 2012. Role of nutraceuticals in human health. Journal of food science and technology, 49(2), pp.173-183. Available At: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/S13197-011-0269-4
Ruchi, S., 2017. Role of nutraceuticals in health care: A review. International Journal of Green Pharmacy (IJGP), 11(03). Available At: https://www.greenpharmacy.info/index.php/ijgp/article/view/1146
Kumar, K. and Kumar, S., 2015. Role of nutraceuticals in health and disease prevention: a review. South Asian J Food Technol Environ, 1(2), pp.116-121. Available At: http://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/43814498/Paper_2-libre.pdf?1458211048
Sosnowska, B., Penson, P. and Banach, M., 2017. The role of nutraceuticals in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular diagnosis and therapy, 7(Suppl 1), p.S21. Available At:https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5418215/
Lopreiato, V., Mezzetti, M., Cattaneo, L., Ferronato, G., Minuti, A. and Trevisi, E., 2020. Role of nutraceuticals during the transition period of dairy cows: a review. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology, 11(1), p.96.
Available At: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s40104-020-00501-x
About the Author
Dr. Ervin Downing is a General Practitioner with over 12 years of experience in primary care. He completed his Medical Degree at Harvard Medical School and pursued his Residency in Family Medicine at the prestigious Mayo Clinic. Dr. Downing is currently practicing at Cleveland Clinic, where he focuses on preventative care, chronic disease management, and holistic patient treatment. His approach emphasizes a personalized, compassionate care plan for individuals of all ages.

