Nutraceuticals bioactive compounds derived from foods that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition have gained global recognition as powerful tools for disease prevention and wellness optimization. As the global nutraceuticals market approaches $636 billion in 2025, driven by aging populations and increased health awareness, understanding their evidence-based benefits becomes essential.
This guide explores how key nutraceuticals support three critical areas of health: immune defense, cardiovascular function, and cognitive performance, based on current scientific evidence.
What Are Nutraceuticals?
Nutraceuticals combine “nutrition” and “pharmaceutical,” encompassing dietary supplements, functional foods, and herbal extracts that deliver therapeutic or preventive health benefits. Unlike pharmaceutical drugs, they're typically regulated as food products, though specific frameworks vary worldwide across the United States, European Union, Canada, and Australia.
Key categories include vitamins and minerals, omega fatty acids, probiotics and prebiotics, plant extracts and phytochemicals, amino acids and proteins, and antioxidants.
Nutraceuticals for Immune System Support
A robust immune system defends against pathogens while maintaining internal balance. Several nutraceuticals demonstrate significant immunomodulatory effects through antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory mechanisms, and microbiome support.
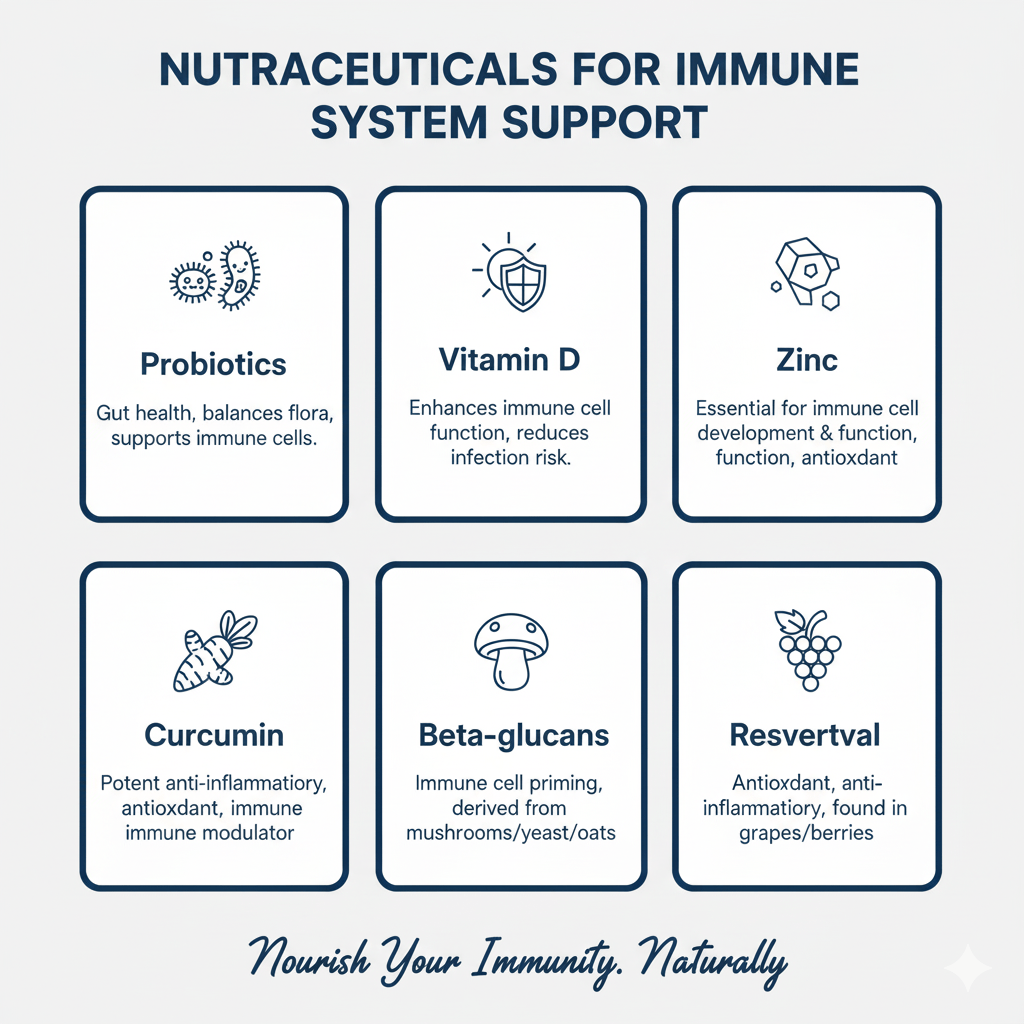
- Probiotics enhance gut barrier integrity, modulate immune signaling, and reduce respiratory infection risk. Clinical evidence shows that specific strains like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium stimulate immunoglobulin A production, activate natural killer cells, and promote regulatory T-cell development. Studies demonstrate that regular probiotic consumption can reduce the duration and severity of common colds and upper respiratory infections.
- Vitamin D regulates both innate and adaptive immunity, with receptors present on immune cells including T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes. Supplementation studies show that adequate vitamin D status (serum levels above 30 ng/mL) supports optimal immune function. Research indicates that 25-100 mcg (1,000-4,000 IU) daily reduces respiratory tract infection risk by 11% in adults.
- Zinc plays essential roles in T-cell development and function, serving as a cofactor for numerous enzymes involved in immune response. Clinical trials demonstrate that zinc supplementation (75-90 mg/day at illness onset) can reduce cold duration by approximately 33% when initiated within 24 hours of symptom onset.
- Curcumin from turmeric suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines including NF-κB, IL-6, and TNF-α while supporting antioxidant defenses. Its immunomodulatory effects help balance immune responses, potentially beneficial for both infections and autoimmune conditions.
Cardiovascular Protection Through Nutraceuticals
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death globally. Evidence-based nutraceuticals targeting lipid profiles, blood pressure, endothelial function, and inflammation offer complementary strategies for heart health.
Evidence-Based Cardioprotective Nutraceuticals
| Nutraceutical | Primary Benefits | Clinical Evidence | Recommended Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 (EPA/DHA) | Reduces triglycerides 20-30%, anti-arrhythmic effects | Multiple clinical trials confirm benefits | 1,000-3,000 mg/day |
| Coenzyme Q10 | Lowers blood pressure, improves heart function | Q-SYMBIO trial: 43% reduction in cardiovascular mortality | 100-300 mg/day |
| Plant Sterols | Reduces LDL cholesterol 5-15% | Systematic reviews confirm effect | 2-3 g/day |
| Garlic Extract | Lowers blood pressure 5-8%, reduces LDL | Meta-analyses support modest BP reduction | 600-1,200 mg/day |
| Magnesium | Regulates vascular tone, reduces stroke risk 10% | Studies link adequate intake to lower CVD risk | 300-400 mg/day |
| Curcumin | Anti-inflammatory, anti-atherosclerotic | Improves endothelial function in trials | 500-2,000 mg/day |
Safety and Practical Considerations
While nutraceuticals generally have favorable safety profiles, responsible use requires awareness of potential interactions and quality concerns.
Nutraceutical Safety Reference
| Nutraceutical | Common Side Effects | Important Interactions | Safe Daily Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Omega-3 | Mild GI upset, increased bleeding time | Anticoagulants, surgery | 1-3 g EPA+DHA |
| Probiotics | Mild initial bloating | Severe immunosuppression | 1-10 billion CFU |
| CoQ10 | Mild GI upset, insomnia if taken late | May reduce warfarin effectiveness | 100-300 mg |
| Curcumin | GI upset, may increase bleeding | Anticoagulants | 500-2,000 mg |
| Ginkgo biloba | Headache, increased bleeding risk | Anticoagulants, seizure disorders | 120-240 mg extract |
| Vitamin D | Nausea with toxicity | Hypercalcemia, kidney stones | 1,000-4,000 IU |
| Garlic | Bad breath, heartburn | Anticoagulants, surgery | 600-1,200 mg extract |
Important Safety Guidelines

Drug Interactions: Many nutraceuticals interact with medications. Omega-3s and garlic may enhance anticoagulant effects. Curcumin can inhibit drug metabolism enzymes. Always inform healthcare providers about all supplements being used.
Quality Verification: Choose products with third-party testing by NSF International, USP, or ConsumerLab. Look for Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) certification.
Appropriate Dosing: Follow evidence-based dosage guidelines. Excessive intake can cause adverse effects. High-dose vitamin D can lead to hypercalcemia, while excessive zinc interferes with copper absorption.
Anti-Inflammatory and Metabolic Health Benefits
Chronic inflammation underlies many modern diseases including obesity, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and arthritis. Several nutraceuticals demonstrate powerful anti-inflammatory and metabolic-regulating properties.
Curcumin suppresses NF-κB activation and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, and COX-2. Clinical trials show curcumin supplementation (1,000-2,000 mg/day) significantly reduces inflammatory markers in conditions like osteoarthritis, metabolic syndrome, and inflammatory bowel disease.
Green Tea Catechins (EGCG) enhance metabolic rate, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce visceral fat accumulation. Studies demonstrate that 400-600 mg of catechins daily can support weight management and improve glucose metabolism in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
Berberine activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), improving insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake. Research shows berberine (900-1,500 mg/day) can lower blood sugar levels comparably to metformin, making it valuable for type 2 diabetes management.
Alpha-Lipoic Acid functions as a potent antioxidant while improving insulin sensitivity. Clinical evidence supports 300-600 mg daily for neuropathy symptoms and blood sugar control.
Digestive Health and Gut Microbiome Support
The gut microbiome influences overall health through immune function, neurotransmitter production, and metabolic regulation. Nutraceuticals supporting digestive health offer wide-ranging benefits.
- Prebiotics (inulin, FOS) feed beneficial gut bacteria, promoting balanced microbiota composition. Consuming 5-10 grams daily of prebiotic fiber enhances Bifidobacteria populations and improves digestive regularity
- Digestive Enzymes (protease, lipase, amylase) support nutrient breakdown and absorption, particularly beneficial for individuals with pancreatic insufficiency or age-related enzyme decline.
- L-Glutamine maintains intestinal barrier integrity, preventing “leaky gut” syndrome. Studies show 5-15 grams daily supports gut healing in inflammatory conditions.
- Ginger Extract reduces nausea, improves gastric motility, and exhibits anti-inflammatory effects in the digestive tract. Clinical trials confirm 1-2 grams of ginger effectively reduces nausea from various causes.
- Peppermint Oil in enteric-coated capsules (0.2-0.4 mL three times daily) relieves irritable bowel syndrome symptoms including abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits.
Implementing Nutraceuticals for Optimal Health
Based on current evidence, nutraceuticals offer valuable support when used appropriately:
- Prioritize food-first approaches: Obtain nutrients from whole foods whenever possible. Supplements work best filling gaps, not replacing balanced nutrition.
- Choose evidence-based options: Focus on nutraceuticals with robust clinical evidence for your specific health goals.
- Ensure quality: Select products with third-party testing verification and transparent labeling.
- Use appropriate dosing: Follow evidence-based recommendations. More isn't necessarily better.
- Monitor effects: Work with healthcare providers to assess effectiveness and safety.
- Think long-term: Nutraceuticals typically work preventively. Consistent use over months is usually necessary for meaningful benefits.
Conclusion
Nutraceuticals Health Benefits represent a powerful bridge between nutrition and medicine, offering evidence-based support for immune function, cardiovascular health, and cognitive performance. From probiotics strengthening gut immunity to omega-3s protecting heart health and DHA supporting brain function, these naturally-derived compounds provide valuable tools for disease prevention and wellness optimization.
The global nutraceuticals market's growth reflects increasing recognition of their therapeutic potential. As research continues revealing mechanisms and benefits, nutraceuticals will likely play expanding roles in integrative healthcare approaches worldwide.
However, their promise must be balanced with responsible use. Quality varies, interactions occur, and not all products have solid evidence. Consumers should prioritize nutraceuticals with robust clinical backing, ensure product quality, use evidence-based dosing, and communicate openly with healthcare providers.
When selected wisely and used appropriately, nutraceuticals offer valuable support for immunity, heart, and brain three pillars of lifelong health and vitality.
Sources
Dillard, C.J. and German, J.B., 2000. Phytochemicals: nutraceuticals and human health. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 80(12), pp.1744-1756. Available At : https://scijournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/1097-0010(20000915)80:12%3C1744::AID-JSFA725%3E3.0.CO;2-W
Ruchi, S., 2017. Role of nutraceuticals in health care: A review. International Journal of Green Pharmacy (IJGP), 11(03). Available At : https://www.greenpharmacy.info/index.php/ijgp/article/view/1146
Durazzo, A., Lucarini, M. and Santini, A., 2020. Nutraceuticals in human health. Foods, 9(3), p.370. Available At : https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/9/3/370
Kumar, K. and Kumar, S., 2015. Role of nutraceuticals in health and disease prevention: a review. South Asian J Food Technol Environ, 1(2), pp.116-121. Available At : https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/43814498/Paper_2-libre.pdf?1458211048=&response-content-disposition=inline%3B+filename%3DRole_of_nutraceuticals_in_health_and_dis.pdf
Das, L., Bhaumik, E., Raychaudhuri, U. and Chakraborty, R., 2012. Role of nutraceuticals in human health. Journal of food science and technology, 49(2), pp.173-183. Available At : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/S13197-011-0269-4
About the Author
Dr. Ervin Downing is a General Practitioner with over 12 years of experience in primary care. He completed his Medical Degree at Harvard Medical School and pursued his Residency in Family Medicine at the prestigious Mayo Clinic. Dr. Downing is currently practicing at Cleveland Clinic, where he focuses on preventative care, chronic disease management, and holistic patient treatment. His approach emphasizes a personalized, compassionate care plan for individuals of all ages.

